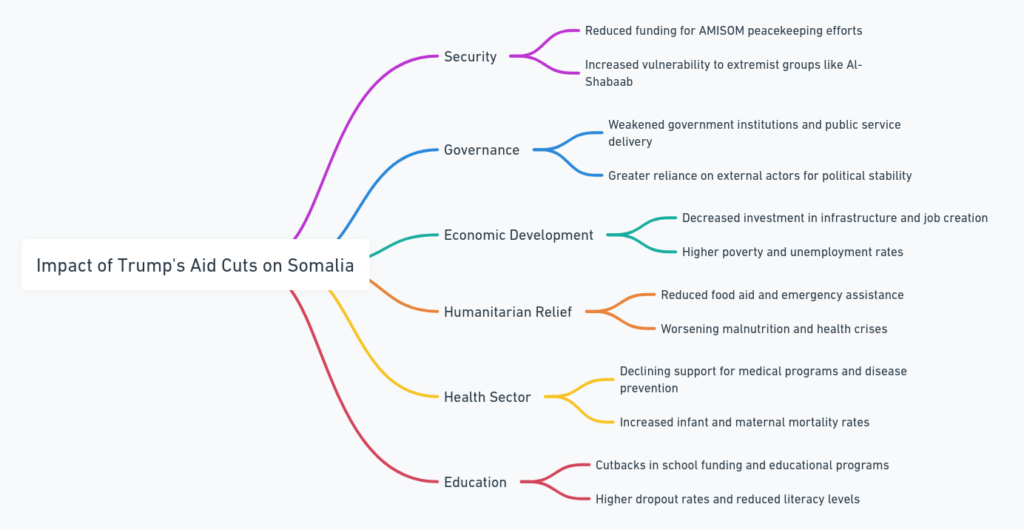
This was the devastating impact of the contemplated U.S. decision to suspend or cut the aid to Africa, given that Somalia is a country fully dependent on foreign intervention for its security, governance, development, and humanitarian intervention. Below is a detailed discussion of the six key areas such an act would affect:
1. Financial Difficulties
Somalia’s economy is weak and heavily dependent on external assistance. Cuts in funding from the U.S. government affected the development programs and implementations in the U.S. Loss of funding translated into some even more serious drawbacks:
• Infrastructure Development Slowdown: Road and port construction, for example, once funded by U.S. development initiatives, slowed down and came to a halt as money became less available, impeding trade and economic growth.
• Less Money on Job Creation:
Somalia’s youth face extremely high unemployment rates and underfunded job and vocational training programs, and poverty increasingly exposes them to the risk of joining extremist groups.
• Impacts on Agriculture: U.S.-funded agriculture development spurred agriculture development to help food production in Somalia. Cuts in funding mean less input into the farmers themselves, increasing imports, and creating a growing concern with food security.
2. Health Repercussions
The U.S. has made considerable contributions to the health industry in Somalia through various programs run by organizations, such as USAID and PEPFAR. Cuts in funding directly impact:
• HIV/AIDS and Malaria programs: Less funds for preventive interventions, life-saving drugs, and health providers.
• Maternal and Child Health Services: One of the highest rates of maternal and newborn deaths is to be found in Somalia. Nutrition, immunization, and prenatal care services were provided via U.S.-funded medical camps. Unfortunately, such increases in deaths were a consequence of the absent programs.
• Emergency Health Response: Without emergency supplies and operating funds, health emergencies in Somalia, such as cholera outbreaks and drought-related malnutrition, were less viable to contain.
3. Stability and Security
Counterterrorism operations, particularly against al-Shabaab, an extremist group in the al-Qaeda mold, were underway in Somalia. The U.S. supplied intelligence, equipment, and training to the Somali government and the African Union Mission in Somalia (AMISOM). The freeze of funds from the U.S. was detrimental to the following:
• Counterterror measures: The less the U.S. support, the less the ability for the Somali security to defeat al-Shabaab. The group was assaulted while the inability of the government to counteract its activities grew.
• Delays In Military Development: The Somali National Army (SNA) relies upon foreign finance and training with greater reliance on the other donors hitherto responsible for supporting the speedy development of an army on their own.
• More Instability: Raids, kidnappings, and violence against civilians and aid workers found fertile ground in the frame of reduced [activity] funding.
4. Repercussions on Diplomatic Relationships
With the cutoff of aid, the U.S. signaled to Somalia and the rest of Africa that it no longer considered cooperation with the continent a priority. Some of the consequences include:
• Tensions between Somalia and the United States: U.S. support gave an injection of legitimacy and cash into the Somalia government. This increase in tension came after financing was terminated, thus forcing Somali officials to search for other sources of authority previously held by the United States.
The more that the role of China-Russia gained influence in Somalia through investments and security cooperation when U.S. influence was on the decline. China, in particular, fostered its influence by creating an increased network of trade as well as financing infrastructure development.
-U.S. influence over the setting of Somali governmental policies has weakened due to the reduction of funds. Increasingly, Washington found it hard to promote anti-corruption as well as human rights advancements.
5. Humanitarian Implications
Somalia was internally displaced due to displacement and starvation caused by recurrent conflict and drought. This intervention received funding for humanity mostly from the U.S., and the intervention would lose significantly when this funding was cut off:
• Growing Food Insecurity: Under the funding of the U.S., WFP was able to feed millions. With dwindling funds came increased hunger and malnutrition among many, especially children.
• Diminished Refugees Support: Internally displaced persons in Somalia are in very large numbers, a great deal of them displaced by conflict and climate change. U.S. support assisted in providing shelter, sanitation, and drinkable water for the internally displaced, as well as support to the refugee camps themselves. Without it, conditions worsen in the refugee camps.
• Lowered Capability of Disaster Response: U.S. support meant a lot in ensuring that humanitarian assistance was provided without delay for disasters, whether caused by floods, locust invasion, or drought. With funding freezes came delays in assistance delivery, thus increasing humanitarian costs. What suffering.
6. Turning Other Influences on Different Authorities
Increased funding from China, Turkey, and the Gulf States came in as the U.S. decreased its presence and influence in Somalia: • China: China has raised its investment in the infrastructure of Somalia, especially concerning highways, marine terminals, and communications. In return, China has lobbied Somalia to support its international diplomatic concerns, like shunning Taiwan.
• Turkey: With one of its largest foreign bases in Mogadishu and important development and humanitarian projects under its auspices, Turkey had a solid presence in Somalia. It greatly assisted in solidifying its position as a critical ally in the international arena after U.S. support was withdrawn.
• Gulf States: Qatar and the UAE, among other states, can bridge gaps resulting from U.S. funding withdrawals in Somalia by providing funds for security operations and government activities. However, the intervention only made things worse, as contrasting factions in Somalia received support from certain Gulf States.
as conclusion words.
Trump’s move to cut or suspend aid to Somalia will have far-reaching ramifications, deepening a long-standing financial predicament, public health challenges, and security threats facing the country. In addition, they helped in the realignment of Somalia towards the Gulf States, China, and Turkey. The overall environment for humanitarian engagements was also negatively affected and hampered relief efforts at a time of disaster, security provision, and displacement.

